Understanding the characteristics of types of companies in Paraguay is essential for choosing the right corporate structure when looking to register a company in Paraguay. Understanding and adhering to all legal and accounting requirements specific to the legal entities in Paraguay is essential for smooth operations and continued compliance. Working with local experts allows you to navigate the regulatory framework with confidence and clarity. Whether opting for flexibility or liability protection, at Biz Latin Hub, we provide the knowledge and support you need to ensure seamless integration into the Paraguyan entrepreneurial ecosystem.
Key Takeaways
| Common legal structure types in Paraguay | Limited Company (Sociedad Anónima – S.A.). Simplified Joint Stock Company (Empresas por Acciones Simplificadas – EAS). Limited Liability Company LLC (Sociedad de Responsabilidad Limitada S.R.L.). Limited Partnership with Shares (Sociedad en Comandita por Acciones). Partnership (Sociedad en Nombre Colectivo). Branch (Sucursal). |
| What is the most common Paraguayan legal structure? | The Simplified Joint Stock Company (EAS) is growing to become the most popular entity type in Paraguay due to the possiblity of establishing one in 72hrs and the protection it offers. |
| What are the primary considerations when choosing a legal entity in Paraguay? | Ownership Structure. Tax Efficiency. Profit distribution. Transfer Pricing. Compliance. Flexibility. |
What are the 6 Most Common Types of Legal Strcutures in Paraguay?
There are various types of legal entities in Paraguay available for foreign investors, these include:
- Limited Company (Sociedad Anónima – S.A.).
- Simplified Joint Stock Company (Empresas por Acciones Simplificadas – EAS).
- Limited Liability Company LLC (Sociedad de Responsabilidad Limitada S.R.L.).
- Limited Partnership with Shares (Sociedad en Comandita por Acciones).
- Partnership (Sociedad en Nombre Colectivo).
- Branch (Sucursal).
To establish an independent legal entity, the company’s by-laws or Articles of Incorporation need to be drafted and signed at the local Notary. Note that identification is needed and in case they also want to act in a managerial capacity, a “Carnet de Radicación Permanente” or Permanent Filing Card must be provided.
A fiscal address for the company needs to be specified as well as the person or people who will administer it.
Keep reading if you are interested in doing business in Paraguay and need to find out about the different types of companies available.
1. Limited Company (Sociedad Anónima – S.A.)
The Sociedad Anónima (S.A.) is one of the most commonly used corporate structures in Paraguay, designed for medium and large businesses that plan to raise capital or operate in regulated industries. This structure is highly versatile and offers limited liability protection to its shareholders, making it an attractive option for both local and foreign investors.
The S.A. allows for the issuance of shares, which facilitates capital-raising opportunities and makes it suitable for businesses that plan to attract multiple investors or operate on a large scale. With a robust governance model typically managed by a board of directors and a general manager, the S.A. ensures professional management and strategic oversight.
One complication that businesses using this structure need to be aware of is that the company would be subject to supervision by the Public Regulator (Equivalent to the SEC in the US).
Key Characteristics and Requirements:
- Shareholders: Requires a minimum of two shareholders, with no maximum limit. Shareholders can be individuals or legal entities, one of them must be a Paraguayan national.
- Liability: Shareholders’ liability is limited to the value of their shares, protecting their personal assets.
- Capital Requirements: A minimum initial capital of PYG 100 million (approximately USD $14,000) is required, with at least 50% paid at incorporation.
- Management Structure: Governed by a board of directors responsible for strategic decision-making and a general manager overseeing daily operations.
- Share Issuance: Shares are freely transferable unless otherwise restricted in the company’s bylaws.
- Legal Requirements:
- Must be registered with the Public Registry of Commerce.
- Requires a fiscal address in Paraguay.
- Appointment of a legal representative is mandatory.
- Taxation: Subject to corporate income tax on income generated in Paraguay.
The incorporation process for this type of entity approximately takes 10-12 weeks to complete.
2. Simplified Joint Stock Company (Empresas por Acciones Simplificadas – EAS)
The Empresa por Acciones Simplificada (EAS) is a modern and flexible corporate structure introduced in Paraguay under Law No. 6480/2020 to promote entrepreneurship and simplify the incorporation of companies. The EAS is specifically designed for small and medium-sized businesses (SMEs), startups, and entrepreneurs seeking a straightforward, cost-effective, and efficient business structure.
The EAS combines the benefits of limited liability with a simplified governance framework, offering significant advantages for businesses that want to reduce administrative burdens while maintaining legal protections. It is particularly attractive because it can be incorporated by a single shareholder and has no minimum capital requirement, making it one of the most accessible corporate structures in Paraguay.
Key Characteristics and Requirements:
- Shareholders:
- An EAS can be incorporated by a single shareholder or multiple shareholders, who can be individuals or legal entities, either local or foreign.
- Shareholders’ identities are required to be registered but remain private from public records.
- Liability:
- Shareholders’ liability is limited to the value of their contributions, ensuring personal assets are not at risk for company obligations.
- Capital Requirements:
- No minimum capital is required. The capital is defined by the shareholders based on the company’s operational needs.
- Capital contributions can be made in cash or kind and must be fully paid at incorporation.
- Management Structure:
- The EAS can be managed by a single director or a board of directors, offering flexibility depending on the size and needs of the company.
- The management structure and decision-making processes are outlined in the company’s bylaws.
- Governance:
- The EAS operates under a simplified governance framework, allowing for faster and easier decision-making.
- Share Issuance:
- Shares can be freely issued and transferred unless restrictions are explicitly stated in the bylaws.
- Legal Requirements:
- Registration with the Public Registry of Commerce is mandatory.
- A fiscal address in Paraguay is required.
- A legal representative must be appointed for administrative and legal purposes.
- Taxation:
- EAS companies are subject to corporate income tax on income generated within Paraguay.
3. Limited Liability Company (Sociedad de Responsabilidad Limitada – S.R.L.)
The Sociedad de Responsabilidad Limitada (S.R.L.) is a business structure designed for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) that prioritize operational control and liability protection. This structure is widely used in Paraguay due to its simplicity and its suitability for family-owned businesses or close-knit partnerships.
The S.R.L. provides limited liability to its partners, ensuring that personal assets are protected. Ownership is divided into quotas rather than shares, and the transfer of these quotas requires the approval of the other partners, preserving the company’s private and controlled nature.
Key Characteristics and Requirements:
- Partners: Requires a minimum of two and a maximum of 25 partners, who can be individuals or legal entities of any nationality, one of them must be a Paraguayan national.
- Liability: Partners’ liability is limited to their contributions.
- Capital Requirements: No minimum capital is required, but all contributions must be fully paid during incorporation.
- Management: Managed by one or more administrators, who can be appointed from among the partners or externally.
- Ownership Transfer: Quotas cannot be freely transferred without the consent of other partners.
- Legal Requirements:
- Registration with the Public Registry of Commerce is mandatory.
- A fiscal address in Paraguay is required.
- Appointment of a legal representative is required.
- Taxation: Subject to corporate income tax on income generated in Paraguay.
4. Limited Partnership with Shares (Sociedad en Comandita por Acciones)
The Sociedad en Comandita por Acciones is a unique corporate structure that combines elements of partnerships and corporations. It is particularly useful for businesses where certain partners want to limit their involvement to financial contributions while others take an active role in management.
This structure features two types of partners: general partners (who manage the business and have unlimited liability) and limited partners (whose liability is restricted to their contributions and who are not involved in daily operations). It is often used in projects requiring both operational leadership and external investment.
Key Characteristics and Requirements:
- Partners: Requires at least one general partner and one limited partner, who can be individuals or legal entities.
- Liability: General partners have unlimited liability, while limited partners are liable only for their contributions.
- Capital Requirements: No minimum capital requirement; contributions can be made in cash or kind.
- Management: General partners handle the management and decision-making. Limited partners do not participate in daily operations.
- Ownership Transfer: Shares held by limited partners can be freely transferred unless restricted by the bylaws.
- Legal Requirements:
- Registration with the Public Registry of Commerce.
- A fiscal address in Paraguay is mandatory.
- Appointment of a legal representative is required.
- Taxation: Subject to corporate income tax on income generated in Paraguay.
5. Partnership (Sociedad en Nombre Colectivo)
The Sociedad en Nombre Colectivo (SNC) is a traditional partnership structure based on mutual trust and shared responsibility among its partners. It is commonly chosen by small businesses, professional firms, or close-knit groups seeking collective decision-making and full operational control.
Unlike other corporate structures, all partners in an SNC share unlimited liability for the company’s obligations. This means that personal assets can be used to cover business debts. While this structure offers operational simplicity, the high level of liability requires a strong level of trust and cooperation among partners.
Key Characteristics and Requirements:
- Partners: Requires at least two partners, who can be individuals or legal entities of any nationality.
- Liability: Partners have unlimited liability for the company’s obligations.
- Management: All partners have equal management rights unless otherwise agreed in the partnership agreement.
- Capital Requirements: No minimum capital requirement; contributions can be in cash, goods, or services.
- Ownership Transfer: Changes in partnership require unanimous consent of the existing partners.
- Legal Requirements:
- Registration with the Public Registry of Commerce is mandatory.
- A fiscal address in Paraguay is required.
- A legal representative must be appointed.
- Taxation: Subject to corporate income tax on income generated in Paraguay.
6. Branch (Sucursal)
A Sucursal (Branch Office) allows foreign companies to establish a presence in Paraguay without creating a separate legal entity. The branch operates as an extension of the parent company, sharing its legal identity and financial liabilities.
The process to incorporate an agency in Paraguay involves the following steps:
- Draft the Company’s by-laws or Articles of Incorporation and sign them at the local Notary.
- Acquire the certificate issued by the Chamber of Commerce of the Country where the Parent Company is based (or its equivalent).
Finally, you’ll need to acquire a Board Meeting Decree or Act from the Parent Company, indicating:
- Clear intent and/or desire to establish the agency in Paraguay
- How much capital the agency will have
- The fiscal address for the agency
- Who will administer the agency
- Granting a Power of Attorney (POA) in favor of the Administrator of the agency.
This structure is ideal for multinational corporations looking to expand their operations into Paraguay while maintaining centralized control from the parent company. Establishing a branch is often faster and simpler than setting up a standalone entity.
Key Characteristics and Requirements:
- Legal Status: The branch is not an independent legal entity; it operates under the parent company’s legal identity.
- Taxation: Subject to corporate income tax on income generated in Paraguay.
- Registration Requirements:
- The branch must be registered with the Public Registry of Commerce.
- The parent company must provide notarized incorporation documents, translated into Spanish.
- Capital Requirements: No minimum capital is required, but the parent company must allocate sufficient resources to the branch.
- Fiscal Address: A registered fiscal address in Paraguay is mandatory.
- Legal Representative: A Paraguayan resident legal representative must be appointed to oversee compliance and operations.
- Bank Account: A local bank account may be required for operational purposes.

Our recommendation: We would recommend establishing an Empresa por Acciones Simplificadas (‘E.A.S’), which is, to some extent, similar to an LLC in the US.
Key Considerations When Choosing Legal Entities in Paraguay
Ownership Structure
Paraguay is a business-friendly destination that allows 100% foreign ownership across most industries. Foreign investors are treated equally to local investors, with no major restrictions in sectors such as manufacturing, agriculture, or services. However, industries like telecommunications, energy, and banking may require specific licenses or government approvals. Companies intending to engage in activities in regulated sectors or the exploitation of natural resources should ensure they comply with sector-specific rules and obtain the necessary permits.
Tax Efficiency
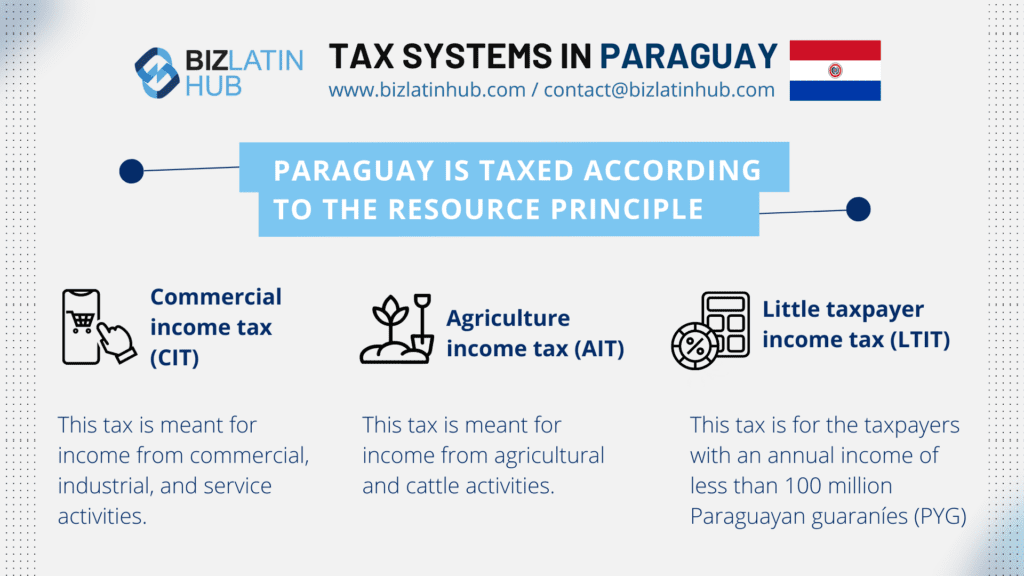
Paraguay operates a territorial tax system, taxing only income generated within its borders. The corporate income tax (Impuesto a la Renta de las Actividades Comerciales, Industriales y de Servicios or IRACIS) is set at 10%, making it one of the most competitive rates in the region. Additionally, there is a 10% Value-Added Tax (VAT) on most goods and services, with reduced rates for essential items. Businesses may benefit from tax exemptions if operating in Free Trade Zones or under the Maquila Law, which incentivizes export-oriented production. Careful tax planning ensures cost efficiency while maintaining compliance with the Paraguayan tax authority (Subsecretaría de Estado de Tributación or SET).
Profit Distribution
Dividends paid to non-residents are subject to a withholding tax of 15%. However, Paraguay has double taxation treaties with countries such as Chile and Taiwan, which can reduce withholding tax rates. Structuring your profit distribution efficiently ensures shareholders maximize returns while minimizing tax obligations.
Transfer Pricing
Paraguay requires businesses involved in cross-border transactions between related parties to comply with transfer pricing regulations. These rules follow OECD guidelines, mandating that intercompany transactions reflect arm’s-length pricing. Companies must prepare and maintain transfer pricing documentation to justify pricing structures, ensuring compliance and avoiding penalties during tax audits.
Compliance
Prepare to meet Paraguay’s compliance requirements. Companies must register with the Public Registry of Commerce (Registro Público de Comercio) and obtain a Taxpayer Identification Number (RUC) from SET. Financial statements must adhere to local accounting standards and, in some cases, to International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS). Businesses are required to file annual corporate income tax returns and submit monthly VAT and payroll tax declarations. Labor compliance is also critical, requiring businesses to contribute to Paraguay’s social security system (Instituto de Previsión Social or IPS) and adhere to local labor laws regarding employee benefits and minimum wages.
Flexibility
Choose a business structure that aligns with your operational goals and allows for scalability and adaptability to future growth. Common legal entities in Paraguay include:
- Limited Company (Sociedad Anónima – S.A.):
A widely used structure for medium to large businesses, offering limited liability protection for shareholders. Shares can be transferred easily, and this structure is ideal for businesses planning to attract investors or raise capital. It requires at least two shareholders and must comply with more formal governance and reporting requirements. - Simplified Joint Stock Company (Empresas por Acciones Simplificadas – EAS):
A modern and versatile structure designed for businesses of any size. The E.A.S. offers single ownership, simplified governance, and fewer corporate formalities. This structure is particularly ideal for startups or companies requiring flexibility to adapt quickly to changes in ownership or capital structure. - Limited Liability Company (Sociedad de Responsabilidad Limitada – S.R.L.):
Best suited for small to medium-sized businesses, the S.R.L. offers limited liability to partners and requires a minimum of two and a maximum of 25 partners. Ownership is divided into quotas rather than shares, and transfer of ownership often requires the approval of other partners, providing more control over ownership changes. - Limited Partnership with Shares (Sociedad en Comandita por Acciones):
A hybrid structure that combines general partners, who have unlimited liability, and limited partners, who are only liable up to the amount of their investment. This structure is ideal for businesses seeking to combine active management by general partners with passive investment by limited partners. - Partnership (Sociedad en Nombre Colectivo):
A partnership structure where all partners share unlimited liability and are jointly responsible for the company’s obligations. This structure is suitable for small, closely held businesses where partners share a high degree of trust and involvement in day-to-day operations. - Branch (Sucursal):
A structure for foreign companies looking to establish a direct presence in Paraguay. The branch operates as an extension of the parent company and is subject to Paraguayan regulations. It provides a simpler incorporation process than forming a separate legal entity while allowing the foreign company to maintain control.

FAQs on Types of Legal Structures in Paraguay
1. Can a foreigner register a company in Paraguay?
Yes, Paraguay welcomes foreign investment and allows foreigners to register companies within its jurisdiction. However, certain regulations and procedures must be followed. Foreign investors may need to appoint a local representative or legal advisor to facilitate the registration process and ensure compliance with local laws.
2. What type of legal entity is Sociedad Anónima (S.A.) in Paraguay?
Sociedad Anónima (S.A.) in Paraguay is a form of corporation where ownership is divided into shares of stock. It offers limited liability protection to its shareholders and is subject to specific regulatory requirements outlined by Paraguayan law.
3. How do I create an LLC in Paraguay?
Creating a Limited Liability Company (LLC) in Paraguay involves several steps, including drafting the articles of organization, defining member rights and responsibilities, registering the company with relevant authorities, and obtaining necessary permits and licenses.
4. What is an LLC in Paraguay?
A Limited Liability Company (LLC) in Paraguay is a business structure that combines the limited liability protection of a corporation with the operational flexibility and pass-through taxation of a partnership.
5. What is the business structure of Simplified Shares Company (S.A.S) in Paraguay?
The Simplified Shares Company (S.A.S) offers a combination of speed, flexibility, and investor-friendly features that make it a suitable choice for foreign businesses looking to establish a presence in Paraguay.
Why Choose to Invest in Paraguay?
Paraguay is a hidden gem for investors, offering one of the most business-friendly environments in Latin America. With low taxes, affordable energy—thanks to abundant hydroelectric power—and a stable economy, the country is ideal for industries like manufacturing, agribusiness, and renewable energy. Its central location in South America provides easy access to key regional markets, supported by improving infrastructure and trade agreements.
Paraguay’s competitive advantages include low operating costs, a young and growing workforce, and untapped opportunities in export-driven sectors. Known for its agricultural strength, the country excels in producing soy, beef, and other high-demand products. For investors looking for growth in an emerging market, Paraguay offers a unique mix of opportunity, affordability, and stability.
Biz Latin Hub can help you With Legal Entities in Paraguay
It’s inevitable that businesses expanding into a new area will encounter complexities within a foreign bureaucratic system during the company formation phase. In Latin America, processes and procedures can vary greatly, and it’s a good idea to seek professional market entry guidance.
At Biz Latin Hub, we help your business move through the formation process smoothly and navigate legal and cultural differences in your new market. Our team of professionals offer a full range of market entry and back-office services to help you manage your investment in Paraguay or another market of choice in Latin America.