Running a business involves understanding the rules that govern employee relationships. In the Bahamas, labor laws shape how business owners engage with their employees. Ignoring these laws can lead to legal complications and financial losses. The Bahamas has specific regulations that cover contracts, wages, safety, leave entitlements, and hiring practices. If starting a business in the Bahamas, you must be aware of these to create a compliant workplace environment. Familiarity with these laws is essential for ensuring smooth operations and protecting both the employer and employees. This guide details the essential requirements for employers under the Employment Act, from contracts and statutory benefits to the legal procedures for termination.
Key Takeaways: Labour Laws in the Bahamas
| What are the main provisions of the Employment Act 2001? | The labor laws in the Bahamas are designed to ensure fair treatment for employees while establishing clear responsibilities for employers. Key aspects include: Working Hours and Overtime Data Retention Policy Hiring and Onboarding Requirements |
| What is the difference between termination for cause and redundancy? | BSD$6.50 per hour or BSD$260 per week. The Bahamian dollar is pegged 1:1 with the USD |
| Types of Employment Contracts in the Bahamas | Indefinite term Fixed term Probationary Part-time |
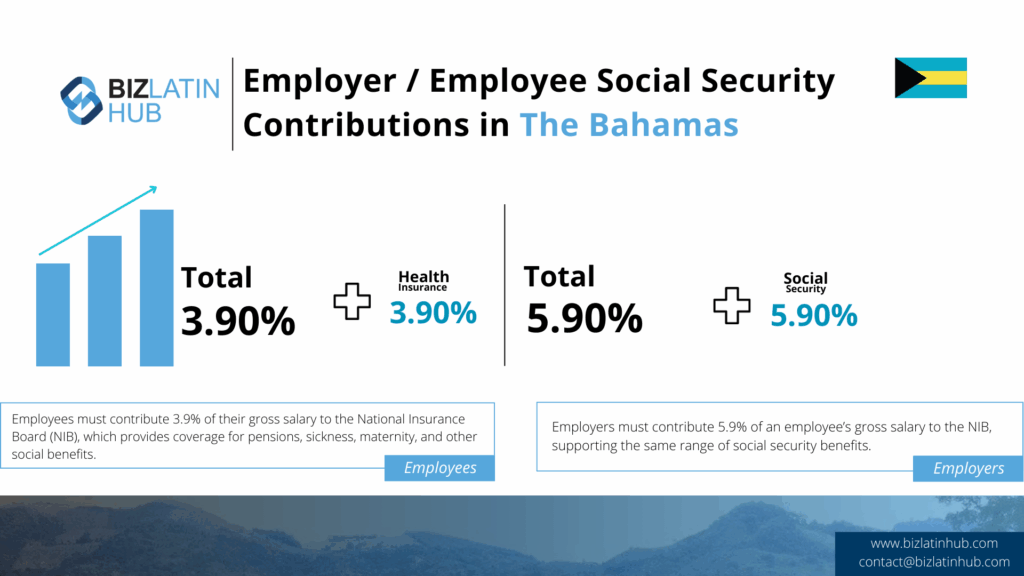
| Percentage of an employee’s salary contributed to social security in the Bahamas | All employers must contribute to the National Insurance Board (NIB). National Insurance contributions are made at 5.9% with the employee adding an additional 3.9%. There are no income taxes to withhold. |
| How much do you pay an employee when terminated? | There are specific rules for calculating redundancy pay. |
| What is the standard work week and overtime rate? | Eight hours daily and up to 40 per week, with additional time compensated at overtime rates. |

Key Obligations Under the Bahamas Employment Act
The employment laws in the Bahamas set clear guidelines for employers and employees. The minimum wage stands at $260 per week. Employers must follow this standard when paying their employees.
According to the Employment Act, 2001, overtime pay is 50% higher than the regular wage. This applies to work beyond 40 hours a week or 8 hours a day. Work on public holidays or rest days earns double the regular pay. Employers cannot require more than 12 hours of work in one day.
Employers need to keep detailed records for each worker. These records include the employee’s name, address, age, wages, hours worked, and vacation claims.
Employment contracts play a critical role in defining employment terms. Both parties need to understand these contracts to meet legal requirements for work hours and termination procedures.
1. Provide a Written Employment Contract
Every employee must be provided with a written contract of employment that specifies the main terms of their job, including wages, hours, and job description.
2. Comply with Minimum Wage and Hours of Work
Employers must pay at least the statutory minimum wage. The standard work week is 40 hours, and overtime rates must be paid for any work performed beyond this limit.
3. Make National Insurance Board (NIB) Contributions
It is a mandatory requirement for employers to register with the NIB and make monthly social security contributions for all their employees.
4. Adhere to Termination and Redundancy Rules
Termination must be for a fair reason, such as misconduct, poor performance, or redundancy. Employers must follow a fair procedure and provide the statutory notice period and any applicable redundancy payments.
Expert Tip: The Legal Definition of Redundancy
From our experience, a frequent and costly mistake made by employers is misinterpreting the term “redundancy.” Under the Employment Act, redundancy has a strict legal definition: it applies only when an employee is dismissed because their position has ceased to exist or the needs of the business for that particular work have diminished.
It is not a general-purpose reason for termination. An employer must be able to prove the role is genuinely redundant. Misclassifying a performance-related dismissal as a redundancy can lead to a successful claim for unfair dismissal at the Industrial Tribunal.
Key Points:
- Minimum Wage: $260 per week
- Overtime Pay: 50% more than regular wages
- Holiday Pay: Double regular wages
- Maximum Working Hours: 12 hours per day
- Record-Keeping: Mandatory for employers
Understanding these laws ensures a smooth employment relationship.
Employment Contracts in Bahamas
Employment contracts in the Bahamas are vital documents. They set out employment terms such as salary, benefits, working hours, and procedures for termination. Both oral and written contracts are acceptable, but written contracts are preferred. Employers must ensure contracts comply with local labor laws, including necessary employee benefits like health insurance and statutory leave. Failure to adhere to labor laws can lead to legal issues.
What are Fixed-Term Contracts?
Fixed-term contracts suit temporary staffing needs. These contracts specify the job’s duration or project timeline with clear start and end dates. Once the term ends, employment ceases without further notice unless the contract states otherwise. Employers use fixed-term contracts to handle temporary increases in workload or specific projects. This helps manage labor costs during demand changes.
What are Probationary Contracts?
Probationary contracts let employers evaluate new hires. The length of the probation isn’t set by law but often lasts a year. During probation, termination can occur without typical notice or severance. Contracts should specify the evaluation criteria for the probation period. No legal requirement exists for probation, but collective agreements might address it.
What are Part-Time Agreements?
The Bahamian Employment Act defines a 40-hour workweek, which helps outline part-time agreements. Part-time employees should receive fair compensation, including potential overtime at 1.5 times the standard rate for over 40 hours a week. Statutory leave policies apply to part-time workers, ensuring paid vacation, sick leave, and other types of leave. Employers must provide meal breaks and a paid weekly rest day. Part-time agreements should clarify work arrangements and benefits to comply with laws.
Minimum Wage Regulations in Bahamas
The Bahamas maintains clear standards for employee wages. The federal minimum wage is $260 BSD per week since 2023. Employers must follow this rule without exception. They must also ensure all employees receive the correct pay for hours worked and are compensated for any overtime.
Current Minimum Wage Rates
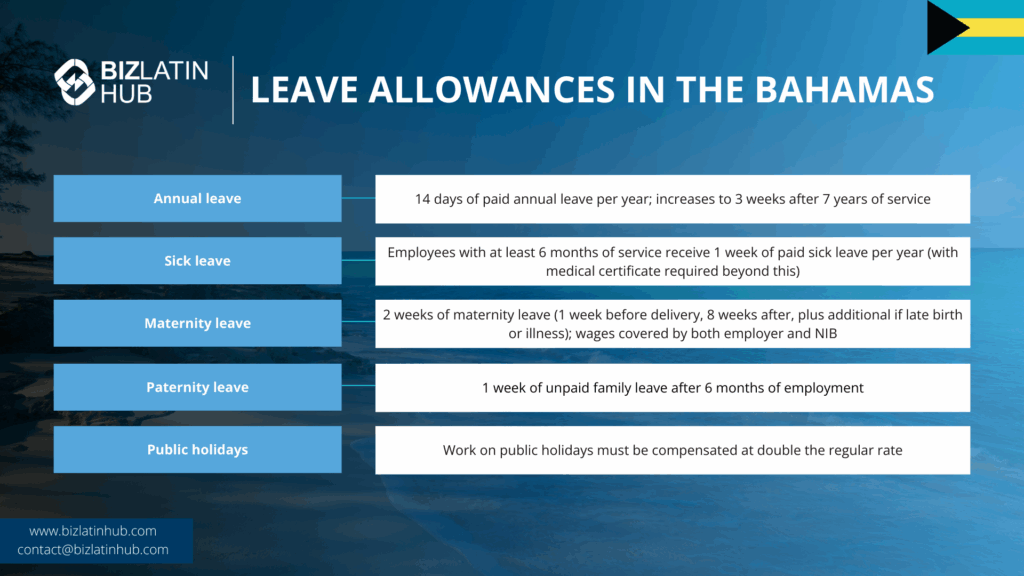
The Bahamas set the minimum wage at BSD$260 per week or BSD$6.50 per hour. This is applied nationwide, without regional differences. Employees receive at least BSD$42 per day. The rule applies to all job types and workers. Holiday pay is given at the standard rate for public holidays, ensuring fair treatment for every worker.
Compliance Requirements for Employers
Employers must adhere to Bahamian labor laws. This includes meeting the minimum wage and keeping detailed employee records. Records must include wages, hours, and vacations for at least three years. Both employers and employees contribute to the National Insurance Board, supporting social security.
Hiring practices must comply with the Employment Act, preventing discrimination in any form. Employment contracts must also reflect legal standards, detailing salary, benefits, and hours clearly. In summary, employers in the Bahamas must respect laws that protect employee rights and ensure fair compensation for their work.
Workplace Health and Safety Standards
Employers in The Bahamas must ensure a safe work environment. This involves following health and safety rules to protect workers from dangers. It’s crucial for employers to use proper safety measures. They must also provide training for a secure workplace.
The law protects employees’ rights. Workers have the right to work without foreseeable risks. They deserve information and training about potential hazards. This knowledge helps them understand the dangers they might face. If a task seems unsafe, workers can refuse it. They should have a good reason to believe it poses a threat to their safety.
General Safety Regulations
In the Bahamas, employees deserve a safe workplace. The law covers this requirement. Workers must receive information on workplace dangers and safe practices. This helps them stay prepared.
Employees can refuse jobs that threaten their safety. This is valid if they have a justified reason. The Department of Labour enforces safety rules. They inspect and check for law violations.
Employers have a duty to apply suitable safety measures. They need to provide training per industry guidelines.
Employee Training and Responsibilities
Employers must handle all paperwork for new hires. This includes employment contracts and other legal forms. This is vital for legal onboarding.
Training new employees is key. It improves job performance and skill development. Training also helps them with job-specific tasks and using needed tools.
Onboarding is more than just legal requirements. It includes making new workers feel part of the team. Emphasizing inclusivity during this time is crucial.
The right onboarding leads to better transitions. When new employees feel prepared and included, they adapt better to their roles.
Below is a basic table outlining key responsibilities for each party:
| Party | Responsibilities |
|---|---|
| Employers | Ensure safe environment, provide training |
| Employees | Understand risks, report unsafe conditions |
| Department of Labour | Inspect and enforce regulations |
This information aids in better understanding Bahamian workplace and safety regulations.
Employee Leave Entitlements Bahamas
In the Bahamas, employee leave entitlements are clearly defined. Employers must provide annual leave, sick leave, maternity leave, and other types as required by law. Full-time employees receive at least 14 days of annual leave per year, which may include public holidays. Regular vacation extends to 3 weeks after 7 years of service.
Sick Leave Provisions
Employees with at least six months of service are eligible for one week of paid sick leave each year. This entitlement cannot roll over or be cashed out. Employees must provide a medical certificate to claim sick leave benefits beyond this period. Sick leave rights ensure workers can recover without financial strain.
Maternity Leave Rights
Female employees are entitled to 12 weeks of maternity leave. This must include at least one week before delivery and eight weeks after. To qualify, they must have 12 months of service with the same employer and not have received maternity pay in the past three years. The National Insurance Board covers 66.66% of average wages. Employers pay 33.33% of wages up to the ceiling amount while on leave. If the birth is late, additional leave covers the time up to delivery, plus six weeks for any related illness.
Paternity Leave Considerations
Male employees can take up to one week of unpaid family leave upon a child’s birth after six months of employment. No paid paternity leave is mandated. This leave reflects support for balancing work and family demands, aligning with Bahamian family-centered values. Employers may offer more generous terms if desired.
The Role of the Department of Labour
The Department of Labour is the government agency in the Bahamas responsible for enforcing employment laws. It assists in the resolution of trade disputes, provides guidance on the Employment Act, and works to ensure fair labour practices are maintained throughout the country.
Hiring Employees in Bahamas
Employers in the Bahamas must prioritize hiring local workers. They should seek approval from the Department of Labor before hiring non-Bahamians. This ensures that no suitably qualified locals are missed. The Employment Act of 2001 provides guidelines for hiring.
Employers must check qualifications, experience, job performance capability, and immigration status. Discrimination based on race, color, religion, sex, national origin, age, or disability is illegal. Employers need to verify immigration status to confirm legal work authorization. Hiring children is banned, except for specific roles listed in Schedule 1 of the Act.
Effective Job Posting Strategies
Effective job postings should be clear and precise. They must state required qualifications and roles as per employment contracts. Employers need to specify the salary range, as the minimum wage is $260 BSD per week. Work hours must be stated, typically 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week.
Benefits like paid vacation should be highlighted: 2 weeks for the first year, 3 weeks after 7 years. It’s important to include the payroll payment cycle, whether bi-weekly or monthly. This sets expectations for potential employees.
Screening Potential Employees
Employers in the Bahamas must give employees a written contract outlining employment terms. Requesting lie detector tests or fingerprints during recruitment is not allowed. The Employment Act of 2001 requires considering qualifications, experience, and ability when hiring. Employers must check immigration status to ensure lawful work capability. Discrimination against race, color, religion, sex, national origin, age, or disability is illegal in the hiring process.
Onboarding Processes
Onboarding is key in the Bahamas to integrate new hires. Employers provide a welcome package including company policies, job responsibilities, and legal requirements. Orientation sessions cover the company’s mission, values, and structure. These help enhance new hires’ understanding and engagement. A good onboarding program speeds up acclimatization and boosts job satisfaction and productivity. Typically, onboarding takes 1-2 working days, depending on information completion and local registrations.
Termination Procedures
In the Bahamas, employers cannot terminate employees at will. They must have a valid reason like misconduct, redundancy, or breach of contract. Employers need to notify employees before termination. Typically, the notice period is two weeks for those employed less than two years and one month for longer service. Employees get severance pay if terminated without cause, amounting to one week’s pay per year of service. Employees can dispute what they see as unfair terminations in labor tribunals. Summary dismissal allows termination without notice in cases of severe misconduct, such as theft or insubordination.
Legal Grounds for Termination
Termination is lawful when based on poor performance, redundancy, or genuine business needs. However, discrimination or retaliation are not valid reasons and are prohibited. Employers must document valid reasons for termination to ensure transparency. The notice period varies by service length—one week’s notice for under a year, and two weeks for one to twelve years of service. Severance pay is calculated as one week’s pay per year of service when terminated without cause. Misconduct such as theft or insubordination justifies termination.
Notice Requirements
Notice requirements in the Bahamas depend on the employee’s length of service. Employees with less than one year get at least one week’s notice. Those with one to twelve years get a minimum of two weeks’ notice. Employees with more than twelve years receive at least four weeks’ notice. Managerial or supervisory roles require one month’s notice regardless of tenure. Employment contracts might specify longer notice periods than the law requires.
Severance Pay Guidelines
The Bahamas does not mandate severance pay, but some employers offer it. Employees with at least one year of service get severance pay if terminated due to redundancy or non-misconduct. It is two weeks’ pay per year for up to 12 years of service, capped at 24 weeks. Managerial staff receive one month’s pay per year worked, with a cap of 48 weeks. Employers should consult the Employment Act of 2001 for all legal aspects of severance pay.
Dispute Resolution Mechanisms
In the Bahamas, clear guidelines regulate the employer-employee relationship. Employers must ensure that employment contracts comply with local labor laws. This helps reduce the risk of legal disputes. Proper employee classification is vital for avoiding misunderstandings that could lead to disputes. Legal services in the Bahamas assist businesses with conflicts involving staff, vendors, or regulatory agencies. Developing sound policies and procedures early can protect companies from future employment disputes.
Internal Dispute Resolution Processes
Employers in the Bahamas must provide written contracts to employees. These contracts detail terms of employment and employee rights. Such documentation aids in resolving disputes internally. Notice periods for termination vary. Employees with less than a year of service get one week’s notice or pay. Those employed over 12 months get two weeks’ notice or pay.
Wrongful dismissal cases can arise if statutory procedures are not followed. This highlights the need for proper procedures. Employees can claim wrongful dismissal if they were terminated improperly or did not receive the required notice. Employers can grant compassionate leave for urgent personal matters, aiding in internal dispute resolution.
Mediation and Arbitration Options
Understanding mediation and arbitration is crucial in maintaining positive employer-employee relationships in the Bahamas. Employment termination is sensitive and requires adherence to legal guidelines for dispute resolution. Disputes from dismissals emphasize the need for clear mediation options to avoid legal issues. Labor unions may mediate during disputes as part of collective bargaining. Effective dispute resolution mechanisms help prevent strikes and labor actions, which can disrupt business operations.
| Dispute Mechanisms | Description |
|---|---|
| Mediation | Involves a neutral third party to facilitate discussion and resolution. |
| Arbitration | A binding process where an arbitrator makes a decision. |
| Internal Resolution | Employs company policies to settle disputes. |
Lists, tables, and well-defined processes ensure clarity for all parties involved.
Work Permits and Visas for Foreign Workers
Foreign nationals who want to work in the Bahamas for more than 90 days must get a work permit. The Bahamas Immigration Department requires specific documents for this process. The Immigration Act states that foreigners need these permits before starting lawful employment. Permits are granted if no qualified Bahamian is available for the role. Fees for these permits range from USD$12,500 annually. The Annual Work Permit is valid for up to one year and can be renewed. Applicants must have a job offer from a Bahamian employer and meet local regulations. The Director of Immigration has the final say in approving permits.
Requirements for Hiring Foreign Employees
Employers must follow strict guidelines to hire foreign workers. The Immigration Act requires them to obtain work permits for non-Bahamians. Approval from the Department of Labor is necessary before hiring. This approval depends on whether qualified Bahamians are unavailable for the job. Work permit costs vary from USD$500 to USD$12,500 per year. The roles usually approved for foreigners include technical, supervisory, or managerial positions. The government encourages foreign business owners to train Bahamians. The aim is for Bahamians to eventually fill technical and managerial roles.
Application Process for Work Permits
The application process involves several steps. Employers need to submit a completed application form. This should include the employee’s passport copy, a medical certificate, and a police certificate. A letter from the employer is needed to explain why a foreign national is preferred over a Bahamian. The Department of Immigration reviews these applications carefully and additional information might be requested.
The Director of Immigration has discretion in granting work permits. Permits are granted based on a valid job offer from a Bahamian employer. There are two types of work permits: short-term permits for up to 90 days and long-term permits for up to one year and renewable.
| Work Permit Type | Duration | Renewable |
|---|---|---|
| Short-term Permit | Up to 90 days | No |
| Long-term Permit | Up to 1 year | Yes |
FAQs about labor laws in the Bahamas
1. What are the labor laws in the Bahamas?
The labor laws in the Bahamas are designed to ensure fair treatment for employees while establishing clear responsibilities for employers. Key aspects include:
- Working Hours and Overtime: Employees cannot work more than 12 hours in a day. Overtime is compensated at time and a half, while work on public holidays is paid at double the standard rate.
- Data Retention Policy: Employers must maintain accurate employee records, including personal details, wages, hours worked, and vacation entitlements, retaining wage records for a minimum of three years.
- Hiring and Onboarding Requirements: The law emphasizes non-discrimination in hiring practices, requiring employers to assess candidates based on qualifications, experience, and skills while prohibiting bias based on race, gender, or other protected characteristics. Employers must verify the immigration status of applicants.
By understanding and complying with these regulations, business owners can foster a fair workplace that supports both employee welfare and economic growth.
2. What is section 29 of the Bahamas Employment Act?
Section 29 of the Bahamas Employment Act addresses the topic of “Maternity Leave.” It provides guidelines for eligible female employees regarding their rights to maternity leave, the duration of the leave, and the conditions under which it can be taken. Specifically, it outlines that a female employee is entitled to at least 12 weeks of maternity leave, which can be taken before and after childbirth.
Furthermore, it states that employees must provide notice to their employer regarding their intended leave and may be entitled to certain benefits during their absence. This section ensures that the rights of female employees are protected while also balancing the needs of employers.
3. What is an employee entitled to when they resign in the Bahamas?
When an employee resigns in the Bahamas, they are entitled to certain rights and benefits based on their employment contract and local labor laws. Key entitlements include:
- Notice Period: Employees are generally required to provide notice of resignation, as specified in their employment contract. The length of this notice period can range from one week to several weeks, depending on the employee’s length of service and the terms outlined in their contract.
- Final Pay: Upon resignation, employees are entitled to receive their final paycheck, which should include any outstanding wages, accrued vacation time, and any other entitled benefits.
- Accrued Leave: If the employee has accumulated vacation or leave days that have not been used, they may be entitled to compensation for those days in their final pay.
- Severance Pay: While severance pay is typically associated with termination, if the employment contract or company policy provides for severance in cases of resignation, the employee may be entitled to this as well.
- References: Although not a legal requirement, many employers provide a reference for employees who resign, which can aid them in future job applications.
It’s essential for employees to review their employment contracts and consult with HR or legal professionals to ensure they fully understand their entitlements upon resignation.
4. Is there a probationary period in the Bahamas?
In the Bahamas, there is no statutory probation period mandated by law. However, collective agreements may include clauses that specify a probation period, which is typically up to one year from the start of employment. This allows both employers and employees to evaluate the suitability of the employment arrangement during that time.
5. What is the minimum wage in the Bahamas?
The minimum wage for private sector employees in the Bahamas is BSD $260 per week.
6. What are the standard working hours?
The standard hours of work are eight hours per day and 40 hours per week. Work performed in excess of these hours must be paid at one and a half times the regular rate on normal workdays, and twice the regular rate on public holidays or rest days.
7. What is the National Insurance Board (NIB)?
The NIB is the social security organization in the Bahamas. Employers and employees are required to make monthly contributions, which fund retirement pensions, sickness benefits, maternity leave, and other social insurances.
8. How is redundancy pay calculated?
An employee terminated for redundancy is entitled to a statutory redundancy payment. For non-managerial staff, this is two weeks’ basic pay for each year of service up to 24 weeks. For managerial staff, it is one month’s basic pay for each year of service up to 48 weeks.
Biz Latin Hub can help you with labor laws in The Bahamas
The Bahamas offers a vibrant business environment with clear employment regulations and a skilled workforce. Our team at Biz Latin Hub brings extensive experience in helping companies navigate the complexities of Bahamian labor laws, work permit applications, and employment contracts. From ensuring compliance with minimum wage requirements to structuring effective dispute resolution mechanisms, we provide comprehensive support for your business expansion needs.
Our local experts can guide you through every aspect of hiring and managing employees in The Bahamas, including contract drafting, payroll management, and visa processing. We understand the nuances of Bahamian employment regulations and can help you build a compliant and successful operation while avoiding common pitfalls that many businesses face when entering this market.
Contact us today to learn how we can support your business expansion in The Bahamas. Our team is ready to help you navigate local employment laws and establish a strong presence in this dynamic market.