Hiring in a foreign country can be daunting. Honduras, with its unique employment laws and culture, presents specific challenges to employers. Understanding these factors is crucial for successful recruitment and retention after company formation in Honduras. The country has employment laws that guide hiring practices, working conditions, and employee rights. Familiarity with these regulations helps prevent legal issues and ensures a smooth hiring process. Employers must also navigate various visa types and local labor market dynamics. This guide provides a step-by-step framework for a successful recruitment process and explains how a Professional Employer Organization (PEO) can manage the legal aspects of employment.
Key Takeaways: Hiring Employees in Honduras
| What are the main steps in the hiring process? | Step 1: Define the Employee Profile Step 2: Conduct the Talent Search Step 3: Interview and Select the Candidate Step 4: Draft the Employment Contract Step 5: Onboard the New Employee Step 6: Manage Payroll and Statutory Contributions |
| Why use EOR services? | An Employer of Record (EOR) can hire employees without a local entity. |
| What are the employer’s obligations to the social security institute (IHSS)? | Employers must register employees with IHSS and contribute around 7% of an employee’s salary to social security, health, and pensions. |
| Are oral contracts recongized? | Yes, but a written employment contract is highly recommended. |
| How can a professional recruitment firm help? | Agencies simplify complex hiring landscapes and ensure compliance with labor laws. |
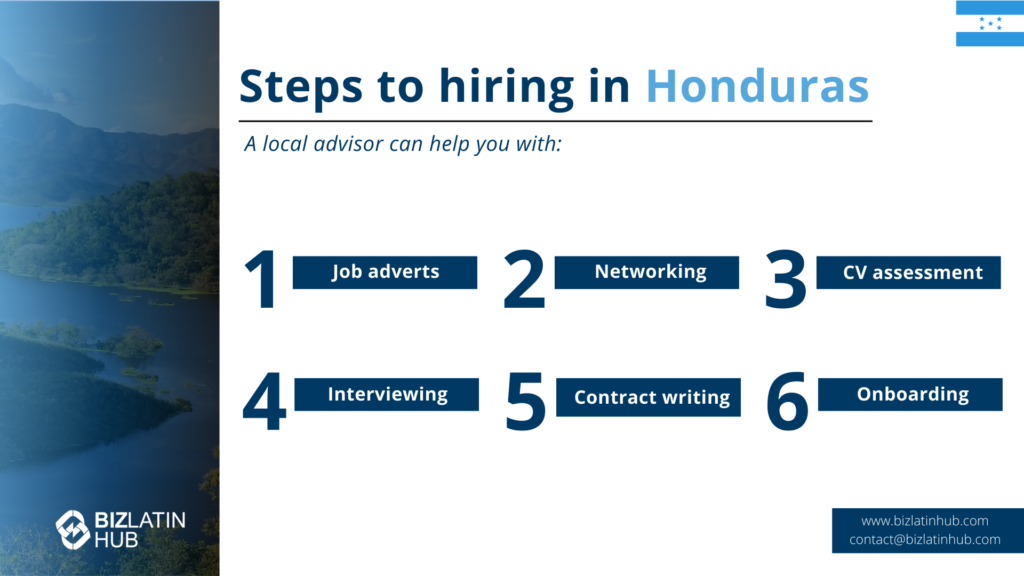
The 6-Step Process for Hiring in Honduras
Step 1: Define the Employee Profile
Create a detailed job description outlining the role’s responsibilities, required skills, and qualifications.
Step 2: Conduct the Talent Search
Source candidates through online job portals, professional networks, or by engaging a local recruitment agency with market expertise.
Step 3: Interview and Select the Candidate
Conduct interviews to assess the skills and cultural fit of the shortlisted candidates before making a final selection.
Step 4: Draft the Employment Contract
Prepare a written employment contract that complies with the Honduran Labor Code and clearly outlines all terms and conditions.
Expert Tip: Including a Clear Probationary Period
From our experience, including a probationary period (período de prueba) in the employment contract is a critical risk management tool for employers in Honduras. The Labor Code allows for a probationary period of up to 60 days.
During this time, the employer can assess the employee’s performance and suitability for the role, and can terminate the contract without liability for severance pay. For this to be valid, the probationary period must be explicitly stated in the written employment contract. We advise all clients to make this a standard clause in their agreements.
Step 5: Onboard the New Employee
Handle all administrative onboarding, including registering the employee with the Honduran Social Security Institute (IHSS).
Step 6: Manage Payroll and Statutory Contributions
Establish a local payroll to process monthly salary payments and ensure the correct deduction and remittance of all social security and tax contributions.
Understanding Employment Laws in Honduras
Understanding employment laws in Honduras is crucial for businesses. The Labor Code is the primary regulation and covers hiring, working, and termination practices. Employers must know the minimum wage, which differs by industry and location.
Working Hours and Wages
- Standard hours: 44-48 per week over six days.
- Minimum wage: Varies by industry and region.
Severance Pay
Severance depends on service length:
- 10 days of salary for 3-6 months.
- 1 month of salary per year, up to 15 months for long-term workers.
Hiring Foreign Employees
To hire foreign workers, employers must prove no local can fill the role. This supports local employment.
Quick Facts:
- Compliance with labor laws is mandatory.
- Employers must manage Social Security contributions and taxes.
- Understanding these laws ensures smooth business operations.
For precise and current details, consulting the Honduran Labor Code or legal advisors is wise. This knowledge helps maintain legal compliance and fosters a fair work environment.
Types of Work Visas Available
In Honduras, several work visas cater to different employment needs. Here are the main types:
- Temporary Work Visa:
- Valid for the duration of the employment contract
- Does not lead to permanent residency or citizenship
- Requires documentation of an employment offer, a valid passport, and proof of financial means
- Permanent Work Visa:
- Granted under specific conditions, typically linked to long-term employment
- Specialized Worker Visa:
- Targeted at individuals with specialized skills or expertise
- Investor Visa:
- For those intending to invest in the Honduran economy
A foreign employee must often obtain a special stay permit. This permit is valid for one to five years. Before it expires, employees should apply for a temporary residence permit. Each type of visa requires submission of specific documents, such as a completed application form and passport-sized photos.
Effective Hiring Practices
Hiring employees in Honduras requires careful planning. Follow these steps for effective hiring:
- Choose Employee Type:
- Independent Contractors: Faster onboarding and flexibility.
- Full-Time Employees: Requires detailed employment contracts.
- Understand Tax Obligations:
- Employers must withhold income tax.
- Remit taxes to Honduran authorities.
- Develop a Recruitment Strategy:
- Allocate budget for advertising and interviews.
- Focus on efficient screening processes.
- Draft Strong Contracts:
- Clearly outline compensation and benefits.
- Include termination procedures.
- Ensure Legal Compliance:
- Adhere to local labor laws.
- Prioritize workplace safety.
Sample Table: Employment Costs
| Cost Type | Details |
|---|---|
| Advertisement | Job postings |
| Interview | Candidate travel |
| Screening | Background checks |
These steps ensure smooth operations and compliance, protecting both employer and employee rights.
Types of Employment Contracts
Honduras offers two primary types of employment contracts: indefinite-term and fixed-term. These contracts regulate how employers and employees interact. They vary based on duration and the nature of the work. Indefinite-term contracts, “contratos por tiempo indefinido,” provide job stability, as they lack a specified end date. Fixed-term contracts, or “contratos por tiempo determinado,” are used for temporary roles, giving clarity on employment duration.
For any employment lasting over 60 days, the Honduran Labor Code requires a written contract. These contracts must detail the employment relationship. However, verbal agreements often cover short-term or domestic jobs under 60 days, showing informality in short-term hires.
Indefinite Employment Contracts
Indefinite-term contracts are the most common in Honduras. They have no fixed end date, offering stability for employers and employees. These contracts typically include benefits like social security coverage and paid vacation days. The law mandates formalizing work intended for more than 60 days in a written contract, either indefinite or fixed-term.
Employees with indefinite contracts have protection under Honduran labor laws. If unfairly terminated, they may receive severance pay. All employment contracts in Honduras must include details such as compensation, benefits, termination procedures, and local labor law compliance.
Fixed-Term Employment Contracts
Fixed-term contracts, or “contratos por tiempo determinado,” serve temporary projects with a clear timeframe. They are suited for roles needing temporary engagement, giving employers flexibility. Unlike indefinite-term contracts, these end when the agreed project or timeline concludes, simplifying termination.
Employers must provide employees with a written explanation detailing contract terms, conditions, benefits, and termination clauses. Like indefinite-term contracts, fixed-term agreements adhere to labor laws about compensation, work hours, and employee rights.
Sample Table: Contract Comparison
| Contract Type | Duration | Termination | Stability | Common Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indefinite | Unlimited | Formal termination | High | Long-term, stable employment |
| Fixed-Term | Specified | End of project/term | Medium | Temporary projects or specific roles |
These formats ensure clarity and compliance, aligning with Honduran labor requirements.
Complying with Local Regulations
Companies operating in Honduras must follow specific laws. The Labor Code governs recruiting and managing workers. Any employment lasting more than 60 days needs a written contract. Contracts can be indefinite or for a fixed term. Key contract clauses include identifying parties, outlining responsibilities, and detailing working hours.
Employers must ensure 90% of their staff are local Honduran employees. Exceptions apply if international hires have unique skills not found locally. Honduran laws prohibit discrimination based on race, religion, politics, or economic status. Keep these regulations in mind when hiring.
Working Conditions Requirements
In Honduras, working conditions are clear. Any job over 60 days must use a written contract. Contracts outline duties and hours. Work hours are capped at eight per day and 44 per week. Overtime requires consent and higher pay.
Both employers and employees contribute to social security. Employers pay about 16.6% of gross wages; employees pay around 8.1%. Additionally, a 13th-month bonus is required. A 14th-month bonus is optional.
Minimum Wage Standards
Minimum wage in Honduras varies by sector and company size. As of January 1, 2024, wages range from HNL 6,762.70 to HNL 13,764 per month. The wage usually translates to $280 to $530 in U.S. dollars. The Ministry of Labor and Social Security reviews wages annually. Compliance with these rates is mandatory to avoid penalties.
| Sector | Company Size | Wage Range (HNL/month) |
|---|---|---|
| Industry A | Small | 6,762.70 |
| Industry A | Large | 13,764 |
Termination Requirements
Terminating employees in Honduras requires just cause. Acceptable reasons include resignation, mutual agreement, or economic necessity. A notice period is needed, varying by service length. New hires require one day’s notice; long-term employees need up to two months.
The Labor Code outlines termination procedures. These include reasons for dismissal and severance entitlements. Employers must follow these rules to avoid legal issues. Ensuring fair treatment is key to respecting employee rights.

Recruitment Landscape in Honduras
The recruitment industry in Honduras is growing due to economic diversification. Sectors like textiles, business processes, and tourism drive demand for workers. Honduras is a leader in apparel manufacturing, exporting goods worth over $11 billion in 2023 to markets like the USA and EU.
Honduras has become a Central American hub for Business Process Outsourcing (BPO). It benefits from a young, tech-savvy workforce skilled in Spanish and English.
Employers must follow Honduran labor laws. This includes drafting employment contracts in Spanish. These contracts detail job roles, employment duration, and termination conditions.
Salaries in Honduras vary by sector. Below is a table of average monthly salaries in different roles:
| Job Role | Average Salary (HNL) |
|---|---|
| Bank Branch Manager | 46,200 |
| Graphic Designer | 17,400 |
Honduran companies attract workers by offering opportunities in diverse industries. The combination of a skilled workforce and economic growth indicates a positive future for recruitment in Honduras.
Using a PEO as an Alternative Hiring Method
A Professional Employer Organization (PEO), also known as an Employer of Record (EOR), is a service that allows you to hire employees in Honduras without first incorporating a local company. Once you select a candidate, the PEO hires them through its own compliant legal entity, managing the employment contract, payroll, and social security contributions.
Using Professional Employer Organization (PEO) services in Honduras offers foreign companies a simple way to hire local employees. A PEO helps manage payroll, taxes, and benefits while ensuring compliance with Honduran labor laws.
Benefits of Using PEO Services:
- Simplified Hiring Process: Onboard international employees quickly and efficiently.
- Legal Compliance: PEOs ensure all employment contracts follow Honduran labor laws.
- Payroll Management: Handle payroll and taxes without setting up a local entity.
- Timely Payments: Ensure employees receive their salaries in their preferred currencies.
Key Considerations:
- Choose a reputable PEO provider with expertise in Honduran employment regulations.
- Communicate your staffing needs and requirements clearly.
The table below summarizes the services EORs provide:
| Service | Details |
|---|---|
| Payroll Management | Handle salaries, tax rates, and Social Security. |
| Compliance | Ensure contracts comply with local labor laws. |
| Benefits | Manage benefits according to Honduran conditions of employment. |
By choosing a reliable PEO, companies can focus on economic growth while reducing administrative burdens.
Hiring Full-Time Employees vs. Contractors
Hiring full-time employees and contractors involves different considerations. Full-time employees often receive benefits such as health insurance, stock options, and paid time off. These benefits enhance their overall compensation. Contractors, meanwhile, can work with multiple companies simultaneously. They are technically self-employed, offering flexibility.
Correct classification of these roles is crucial. Misclassification can lead to penalties. Collaborating with an Employer of Record (EOR) helps ensure compliance. The EOR handles onboarding and payments according to local labor laws.
When deciding between full-time employees and contractors, consider your company’s hiring strategy. Reflect on the nature of the work and the level of control needed over performance.
Key Considerations
| Full-Time Employees | Contractors |
|---|---|
| Receive employee benefits | Have the flexibility to work elsewhere |
| Enhanced compensation package | Self-employed status |
| Require correct classification | Require correct classification |
Hiring Strategy Tips
- Align the decision with internal goals
- Evaluate the need for employee benefits
- Ensure legal compliance through proper classification
Choosing between full-time employees and contractors impacts your business identity and operational success.
Labor Taxes and Payroll Considerations
Employers in Honduras face several labor taxes and payroll obligations. They must contribute an extra 9.87% on top of salaries for public health insurance and a housing fund. Additionally, employers pay 13th and 14th salaries, each equal to one month’s salary, in December and July.
Withholding and remitting income tax falls on employers. Tax rates range from 0% to 25%, based on income brackets. Employees receive a minimum of 10 paid holidays after one year. This increases up to 20 days after four years.
Sick leave is available after three days of illness. Employees can receive up to 26 weeks of paid leave per year at 66% of their average salary.
Payroll Obligations:
- Public Health Insurance and Housing Fund: +9.87% of salary
- 13th and 14th Salaries: One month’s salary each in December and July
- Income Tax: 0% to 25% based on income
- Public Holidays: 10-20 days based on tenure
- Sick Leave: 66% pay for up to 26 weeks
These requirements ensure compliance with Honduran labor laws and employee benefits.
Insights into Local Work Culture
Honduran workplace communication is direct yet polite. Building personal relationships is vital in business interactions. The local work culture maintains a clear hierarchical structure. Respect for seniority and authority is important among employees.
Hondurans value work yet prioritize family time. Employees often expect flexibility for family obligations. Community and collective responsibility are key cultural values.
To foster teamwork, consider these steps:
- Include activities to build a sense of belonging
- Encourage open communication
- Recognize individual and team achievements
By embracing these cultural values, employers can create an inclusive work environment. This approach enhances employee engagement, satisfaction, and retention. Here is a quick overview:
| Key Values | Implementation |
|---|---|
| Personal Relationships | Foster team activities |
| Hierarchy | Respect for authority |
| Family Priority | Offer flexible working conditions |
| Community and Teamwork | Encourage collective responsibility |
Understanding these insights can improve workplace dynamics and productivity.
Building a Strong Workforce
Honduran culture values community and collaboration. Employers should focus on creating a sense of belonging and teamwork. This approach boosts engagement and retention among employees.
The workforce in Honduras features well-educated young women. They often have more post-secondary education than young men. Employers should consider this demographic when hiring for positions that need higher education.
The standard workweek in Honduras is 44 hours. Employers must adhere to this regulation to keep a healthy work environment. Part of legal compliance involves contributing to social security. These contributions cover sickness, maternity, old age, and unemployment benefits.
Effective communication is crucial for a positive work atmosphere. In Honduras, communication can be indirect. Employers should adjust their style to ensure understanding.
Remote Hiring Strategies
Hiring remote workers outside Honduras involves specific regulations. Employers must follow local tax and labor laws if hiring through a Honduran company. It’s vital to track work permit renewal deadlines to avoid legal status gaps.
The work permit and visa application process requires several documents. Employers must submit employment contracts, proof of qualifications, and health certificates. When applying for foreign worker permits, employers must show no suitable local candidates are available.
Misclassifying contractors as full-time employees can lead to penalties. Ensure correct classification to avoid such fines.
Establishing a Local Entity
Creating a local entity in Honduras requires several steps. Companies must submit details to the Commercial Registry, the Honduran Social Security Institute, and the Ministry of Labor and Social Security.
Obtaining a Registro Tributario Nacional, a tax identification number, from the Servicio de Administración de Rentas is essential.
The process can take weeks and involves significant fees. Once established, businesses can recruit using platforms like Tecoloco, Empleos.net, and Computrabajo.
Having a local entity reduces risk and enables direct hiring. However, it can be costly and time-consuming, so it may not suit companies seeking quick hiring solutions.
Onboarding Processes
The onboarding process in Honduras focuses on integrating new hires into the organization. It ensures they understand their roles and align with company culture. Employers prepare ahead of a new hire’s first day by drafting employment contracts and gathering necessary paperwork, such as identification and tax forms.
The minimum onboarding time can be as short as 1-2 working days. This depends on how quickly required information is submitted and local authority registrations are completed. For non-nationals, this timeline may extend by up to three additional days for the Right to Work assessment, with possible delays for follow-ups.
Proper onboarding includes filing relevant employee documents and setting up payment methods. This process can be streamlined with services like Globalization Partners or Skuad.
Key Onboarding Steps in Honduras:
- Draft employment contracts.
- Gather identification and tax forms.
- Register with local authorities.
- Complete Right to Work assessment (for non-nationals).
- File employee documents.
- Set up payment methods.
Streamlined onboarding helps new employees start efficiently and aligns them with their new roles and responsibilities.
Best Practices for Employee Retention
Employers in Honduras should offer additional benefits to retain employees. Bonuses, health insurance, and retirement plans increase job satisfaction. This satisfaction fosters long-term commitment.
Ensure compliance with wage regulations and contribute to the Instituto Hondureño de Seguridad Social. This obligation provides employees with stability and security. It also shows a commitment to supporting their well-being.
Invest in training programs to equip employees with needed skills. Training demonstrates commitment to professional development. This can lead to increased employee loyalty.
Effective recruitment is vital. Advertise job openings well and carefully screen candidates. Align hiring decisions with company goals. This step enhances employee retention.
Tax compliance and social security contributions build trust. Legal employment practices demonstrate commitment to employee welfare.
Checklist for Best Practices
- Offer additional benefits like bonuses and insurance.
- Follow wage regulations.
- Contribute to Social Security.
- Invest in employee training programs.
- Advertise and screen job candidates properly.
- Ensure compliance with tax laws.
These steps support a positive work environment and improve retention.
Frequently Asked Questions: Hiring in Honduras
What are the key employment laws in Honduras?
Employment laws in Honduras protect worker rights. These laws include minimum wage, maximum working hours, and workplace safety. Enforcement varies across sectors. The standard workweek is 44 hours, with a daily cap of eight hours. Employment contracts must be in writing for positions lasting over 60 days. These contracts detail rights, responsibilities, working hours, and termination procedures. Female employees receive 10 weeks of maternity leave, covering four weeks before and six weeks after childbirth. Termination requires legal cause such as economic necessity or disciplinary reasons.
Is a written employment contract required?
While verbal contracts can be recognized, a written contract is the standard business practice and is highly recommended. It provides clear proof of the terms of employment and is essential for enforcing key clauses like a probationary period.
What is a PEO?
A PEO, or Employer of Record (EOR), is a third-party organization that legally employs staff on your behalf. It’s an ideal solution for businesses that want to hire in Honduras without the time and expense of setting up a local company.
What is the Honduran Social Security Institute (IHSS)?
The IHSS is the government body that manages the social security system in Honduras. All employers must register with the IHSS and make monthly contributions for their employees, which covers health, disability, and pension benefits.
What is the “thirteenth and fourteenth month” salary?
In Honduras, it is mandatory for employers to pay two annual bonuses. The “thirteenth month” salary is paid in December, and the “fourteenth month” salary is paid in June. Each bonus is equivalent to one month’s wages.
Biz Latin Hub can help you with hiring in Honduras
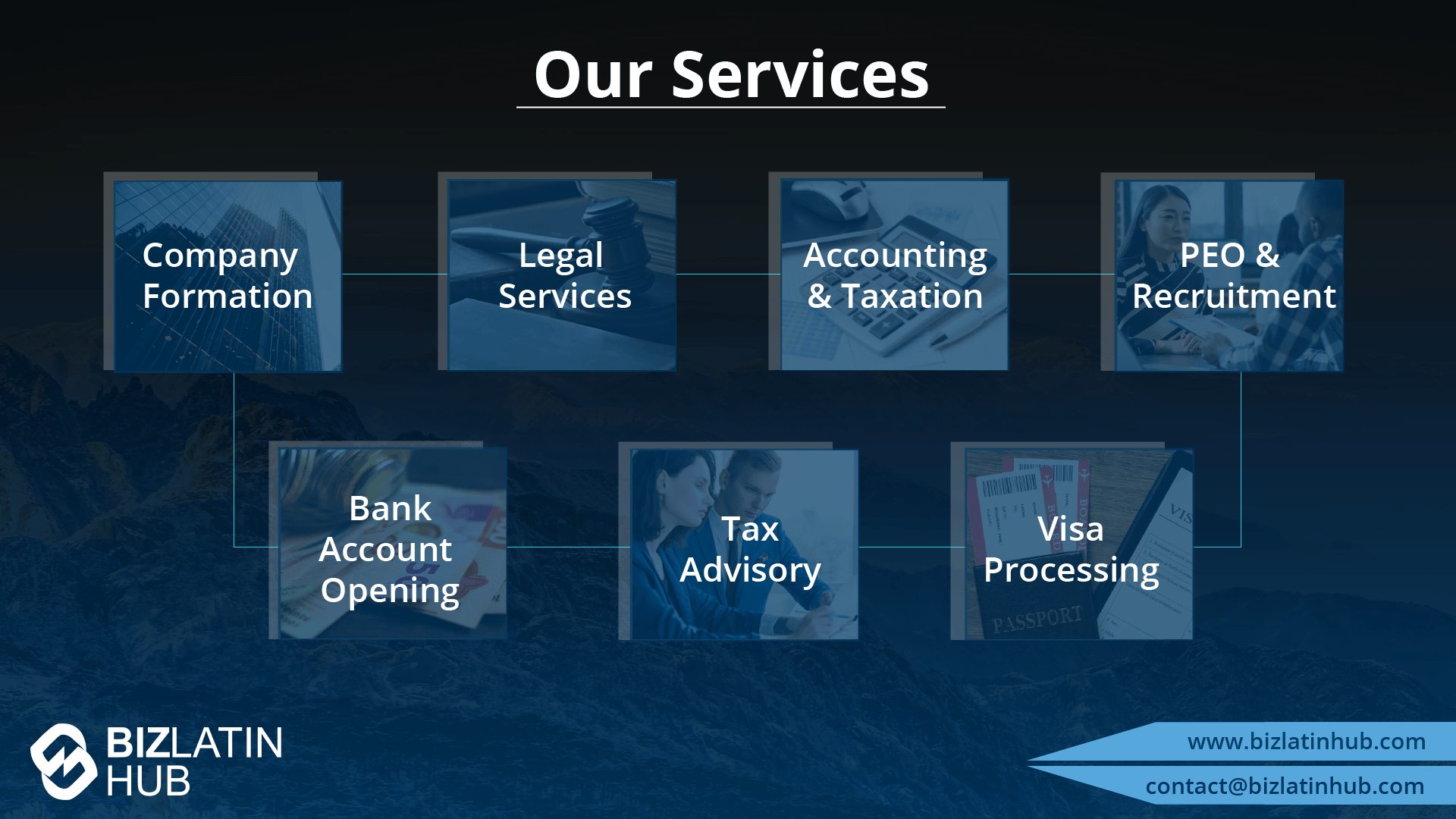
At Biz Latin Hub, our multilingual team of company formation specialists has extensive experience in supporting foreign executives when starting a business in Latin America. We offer a complete set of services for your business needs, such as legal, accounting, and recruitment support.
You can rely on us as your main contact for entering and doing business in any of the 18 markets in Latin America and the Caribbean where we operate.
Contact us now for personalized assistance or a free quote on company formation in Latin America.
Learn more about our team and expert authors.