Before investing in and starting a business in Nicaragua, you must understand the local corporate business laws. Otherwise, you risk suffering severe legal penalties and reputational damage in the region. Learn more about Corporate Legal Compliance Nicaragua. When it comes to accounting and taxation in Nicaragua, many regulations must be followed. There must be strict compliance with tax rates and tax filing dates. This guide details the essential requirements for all Nicaraguan corporations, including record-keeping, tax filings, and mandatory meetings.
Key Takeaways: Corporate Legal Compliance in Nicaragua
| What are the three mandatory corporate books a company must maintain? | Every company must keep three official books: a Journal Book, a Ledger Book, and a Minutes Book |
| What annual taxation records must companies keep? | Companies must file an annual income tax return with the DGI. |
| What is the role of the company’s legal representative in Nicaragua? | A designated legal representative has the legal authority to act on behalf of the company and sign official documents. |
| Are there any annual renewals to handle? | A municipal business license must be renewed each year. |
| What is the Public Mercantile Registry? | The Public Mercantile Registry is where the company’s incorporation deed and all subsequent corporate resolutions are recorded. |
Key Compliance Requirements in Nicaragua

1. Maintain Official Corporate and Accounting Books
Every company must keep three official books: a Journal Book, a Ledger Book, and a Minutes Book for shareholder and board meetings. These books must be authorized by the relevant authorities before use.
Expert Tip: Stamping and Sealing Corporate Books
From our experience, a critical but often overlooked step is the official authorization of corporate books. Before any entries are made, the three main books (Journal, Ledger, and Minutes Book) must be presented to the DGI for stamping and to the Mercantile Registry for sealing.
We have seen companies face significant issues because they began recording minutes or transactions in unauthorized books, which renders the records legally invalid. Always ensure your books are officially authorized immediately after incorporation and before any business activity commences.
2. Hold an Annual Shareholders’ Meeting
An ordinary shareholders’ meeting must be held once per year to approve financial statements and appoint the board. All resolutions must be recorded in the official Minutes Book.
3. Fulfill Tax Obligations
Companies must register with the DGI, make monthly provisional income tax payments, and file an annual definitive income tax return.
4. Appoint a Legal Representative
All companies must have a designated legal representative who has the legal authority to act on behalf of the company and sign official documents.
5. Renew Municipal Registrations
Businesses must register with the municipality where they operate and renew their registration and business license annually.
Tax rates in Nicaragua
Understanding accounting and taxation in Nicaragua is vital when launching a business in this market. Here are the tax rates you must be aware of.
Income Tax: Nicaragua taxes its citizens and all residents and non-residents on their income sourced in Nicaragua. Residents are subject to income tax according to the progressive tax rates shown below:
- If your income is between 0 and 100,000 NIO, you won’t pay any taxes.
- For income between 100,000 and 200,000 NIO, you’ll pay 15% on the amount over 100,000 NIO.
- If you earn between 200,000 and 350,000 NIO, you’ll pay 15,000 NIO plus 20% on the amount over 200,000 NIO.
- Income between 350,000 and 500,000 NIO will incur a tax of 45,000 NIO plus 25% on the amount over 350,000 NIO.
- For income over 500,000 NIO, you’ll pay 82,500 NIO plus 30% on the amount over 500,000 NIO.
Corporate Tax: Corporate Income Tax (CIT) in Nicaragua applies solely to income earned domestically. It’s calculated at a flat rate of either 30% of net taxable income (total taxable income minus allowable deductions) or a minimum tax rate of 1% to 3% on gross income earned during the fiscal year. The higher of these two amounts is the tax due.
Value Added Tax (GCT): The following transactions are taxed under VAT:
- Sale of goods
- Provision of services
- Importation of goods
- Exportation of goods and services
A 15% VAT rate applies to goods sold, services provided, asset use, and imported goods. However, exports of goods and services are taxed at a 0% rate.
Certain items are exempt from VAT, such as medicine, real estate transfers, used goods sales, basic food products, credit instruments, tuition, textbooks, and educational supplies.
Withholding Tax: When non-resident corporations receive payments for dividends, interest, royalties, or service fees in Nicaragua, they’re subject to withholding tax (WHT) as outlined below:
- Dividends: 15%
- Interest:
- For non-financial companies: 15%
- For financial companies: 15%
- Royalties: 15%
- General services: 20%
- TV and radio programming or subscription: 15%
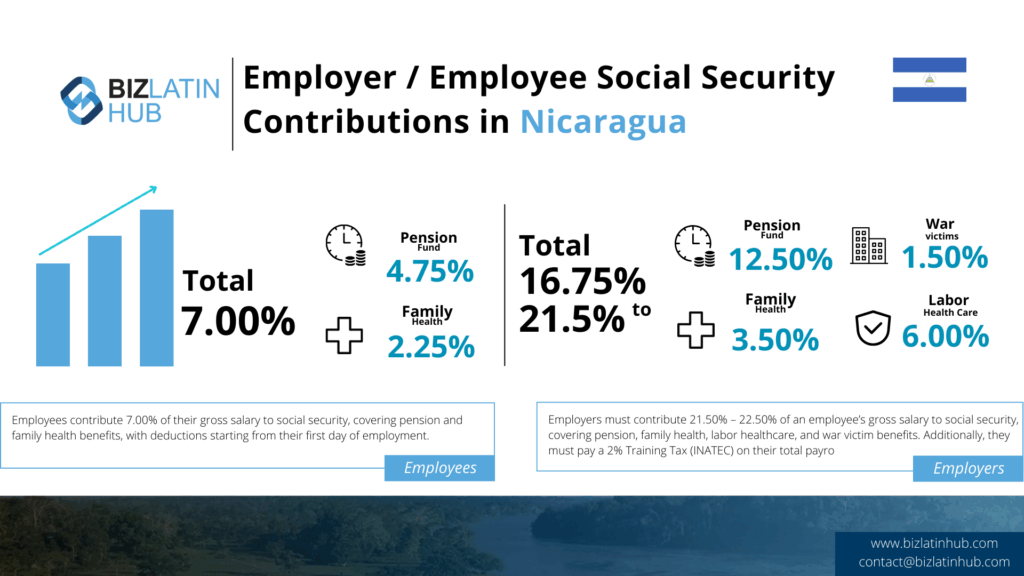
Social Security: Social Security contributions are deducted from the gross salary of employees every month, starting from the first day of employment. The rates for different benefits are as follows:
- Pension: Employer contributes 12.50% (or 13.50% for larger employers), and employee contributes 4.75%.
- Family health: Employer contributes 6.00%, and employee contributes 2.25%.
- Labor healthcare: Employer contributes 1.50%, and employee contributes 0%.
- War victims: Employer contributes 1.50%, and employee contributes 0%.
- Total: The combined contribution rates range from 21.50% to 22.50% for employers and 7.00% for employees.
Additionally, employers must pay a monthly Training Tax (INATEC) of 2% of their payroll.
What is the Tax Structure in Nicaragua?
In Nicaragua, the tax system is territorial, meaning only income earned within or affecting Nicaragua is typically taxed. Corporate income tax (CIT) applies to a company’s profits, including business/trading income and passive income.
Capital incomes and gains are subject to withholding tax (WHT). General business expenses are deductible when calculating taxable income.
Tax Payment
Corporations are required to make monthly advance payments towards their fiscal-year income tax obligations. The amount payable each month is determined as a percentage ranging from 1% to 3% of the gross income.
The final payment of Corporate Income Tax (CIT) is due concurrently with the submission of the final CIT return. This deadline falls within two months after the conclusion of the fiscal year.
Tax Audit Process
Tax audits may be initiated by the tax authorities as deemed necessary. It is incumbent upon the taxpayer to furnish the tax auditor with all relevant corporate information and documents of income generation.
The Role of the DGI and Mercantile Registry
Two main bodies oversee corporate compliance in Nicaragua. The Public Mercantile Registry is where the company’s incorporation deed and all subsequent corporate resolutions are recorded. The General Directorate of Revenue (DGI) is the national tax authority responsible for collecting corporate income tax and other duties.
International Tax Treaties in Nicaragua
Nicaragua does not have a bilateral income tax treaty with any other country.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Accounting and Taxation in Nicaragua:
Using our experience, we’ve identified common questions and worries our clients often have when dealing with accounting and taxation in Nicaragua.
1. What is the corporate income tax rate in Nicaragua?
The corporate income tax rate is 30% on net income. There is also a definitive minimum payment of 1% to 3% of gross income, and companies must pay whichever amount is higher.
2. How does VAT work in Nicaragua?
VAT (Value Added Tax) in Nicaragua is levied at a standard rate of 15% on the sale of goods, provision of services, asset use, and import of goods. Exports of goods and services are taxed at a 0% rate.
3. What are the withholding tax rates for non-resident corporations in Nicaragua?
Withholding tax rates for non-resident corporations in Nicaragua vary depending on the type of payment. For dividends, interest, royalties, and service fees, the rates range from 15% to 20%.
4. How are social security contributions calculated for employees in Nicaragua?
Social security contributions in Nicaragua are calculated based on the gross salary of the employee. Contributions cover pension, family health, labor healthcare, and war victims’ benefits, with rates ranging from 0% to 12.50% for employees and 7.00% to 22.50% for employers.
5. What are the requirements for annual financial reporting in Nicaragua?
Annual financial reporting requirements in Nicaragua depend on the type and size of the entity. Generally, companies are required to prepare and file audited financial statements within a specified timeframe.
6. Are there any tax incentives available for businesses in Nicaragua?
Nicaragua offers various tax incentives to promote investment and economic development. These incentives may include tax holidays, reduced tax rates, and exemptions for specific industries or activities. For example, businesses investing in infrastructure projects, such as roads, ports, energy, and telecommunications, may qualify for tax exemptions on income generated from these projects.
7. What happens at the Annual Shareholders’ Meeting?
The Annual Shareholders’ Meeting is held to approve the financial statements from the previous year, decide on the distribution of profits, and appoint or ratify the Board of Directors and the official Vigilance Officer.
8. Does the legal representative have to be a Nicaraguan citizen?
No, the legal representative does not have to be a Nicaraguan citizen. However, a foreigner appointed as a legal representative must have legal residency in Nicaragua.
9. What is the purpose of the Vigilance Officer?
The Vigilance Officer (Vigilante) is a unique role in Nicaraguan corporations. This person is appointed by the shareholders and is responsible for overseeing the company’s administration. They have unlimited rights to inspect the company’s books and operations to ensure everything is being managed correctly on behalf of the shareholders.
Biz Latin Hub Can Support Your Corporate Legal Compliance In Nicaragua
Biz Latin Hub offers comprehensive market entry and back-office support across Latin America and the Caribbean, with a presence in key cities.
We also have trusted partners in many other markets. Our unmatched reach means we are ideally placed to support multi-jurisdiction market entries and cross-border operations.
As well as our extensive knowledge of accounting and taxation in Nicaragua, our range of services includes hiring and PEO, accounting and taxation, company formation, bank account opening, and corporate legal services.
Contact us now to learn more about how we can assist you in finding top talent or doing business in Latin America and the Caribbean.
If you found this article on accounting and taxation in Nicaragua useful, check out the rest of our regional coverage. Or read about our team and expert authors.