Choosing the right business structure is crucial for any entrepreneur. It can determine your legal liabilities, tax obligations, and growth potential. Understanding the options available in Nicaragua can simplify this decision-making process.
Nicaragua offers several business structures, each with unique advantages and disadvantages. Entrepreneurs must consider factors like liability, taxation, and regulatory requirements when selecting a structure. This knowledge ensures that business owners make informed choices that align with their goals.
In this article, we will explore the various business structures available in Nicaragua, focusing on corporations, limited liability companies (LLCs), and sole proprietorships. We aim to equip you with the essential information needed to make the best decision for your business.
Importance of Choosing the Right Business Structure in Nicaragua
Choosing the right business structure in Nicaragua is crucial for business success. It influences operational processes and legal compliance, particularly for foreign branches. Here are some common business structures:
- Limited Liability Companies (LLCs)
- Favored by foreign investors.
- Allows capital contributions as participations.
- Offers flexible ownership.
- Corporations
- Enhance credibility among suppliers and partners.
- Require rigorous accounting practices.
- Offer potential tax exemptions.
- Allow access to investment protection agreements.
- Facilitate public and private contract access.
Table: Key Features of Business Structures in Nicaragua
| Structure Type | Ownership Flexibility | Credibility | Compliance Needs | Tax Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LLC | High | Medium | Moderate | Flexible |
| Corporation | Medium | High | High | High |
Choosing a suitable structure not only affects daily operations but also long-term growth and profitability. Corporations offer additional benefits like enhanced credibility and access to significant contracts. Select wisely to align with your business goals.

Corporations
Corporations, or sociedad anónima (S.A.), are the most common legal entity type in Nicaragua for business operations. These entities focus on capital divided into shares. Shareholders benefit from limited liability. They are personally liable only up to their capital contributions.
Incorporating a Corporation in Nicaragua takes about 30 days. This timeframe allows entrepreneurs to start their business quickly. The minimal share capital requirement is zero. This setup enables starting a business without initial capital investment.
A Corporation is formed by pooling capital from shareholders. Managed by revocable agents, Corporations follow Nicaraguan commercial law. These agents act under a defined company purpose.
Here’s a quick overview:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Entity Type | Corporation (S.A.) |
| Liability | Limited liability for shareholders |
| Incorporation Time | Approximately 30 days |
| Minimum Capitalization | Zero |
| Management | Revocable agents under a defined company purpose |
Corporations provide a flexible and appealing structure for businesses. They allow quick setup and protect personal assets, aligning with the economic activities and goals of companies in Nicaragua.
Limited Liability Companies (LLCs)
Limited Liability Companies (LLCs) in Nicaragua, known as “sociedades colectivas de responsabilidad limitada,” are formed based on partner contributions. This setup offers a flexible management style. It also protects personal assets from company liabilities. An LLC in Nicaragua does not need to deposit a minimum share capital in a bank, easing business entry.
Key Features of LLCs in Nicaragua:
- Formation Basis: Partner contributions instead of shares.
- Owner Protection: Personal assets shielded from company liabilities.
- No Minimum Share Capital: Simplifies starting a business.
Incorporating a Sociedad Anónima (S.A.) in Nicaragua, a related entity, takes about 30 days. The country’s Commercial Code governs LLCs. It outlines necessary procedures for their creation and operation.
An LLC provides a beneficial structure for economic activities. It encourages participation without significant initial financial hurdles. This makes LLCs an attractive choice for entrepreneurs.
Sole Proprietorships
A Sole Proprietorship is the simplest business entity. It is owned and managed by a single individual. This structure is the easiest way to start a business.
In India, a sole proprietorship is not regulated by any specific law. The owner has complete control over decision-making and management. This flexibility attracts many entrepreneurs.
Registration for a sole proprietorship in India requires basic documents. These include:
- Aadhar card
- PAN card
- Bank account details
- Proof of a registered office
Unlike more complex business structures, a sole proprietorship does not need a formal setup. This lack of complexity simplifies the startup process. Sole proprietors can conduct business activities independently. They do not need shareholders or partners.
This business form suits those seeking ultimate control and simplicity. A sole proprietorship allows swift decision-making and easy management.
Advantages of Incorporating as a Corporation
Incorporating as a corporation in Nicaragua can offer many benefits. It provides access to public and private contracts. This is significant because many tenders require companies to be incorporated. The legal system in Nicaragua offers tax exemptions and reductions for corporations. These benefits make operations more efficient and profitable.
A corporation allows for strong corporate governance practices. Improving internal management enhances the company’s reputation. Corporations follow stricter regulations. This shows a commitment to legal and fiscal compliance, boosting stakeholder trust. The corporate structure also offers more flexibility and growth opportunities for foreign investors.
Limited Liability Protection
In Nicaragua, a Limited Liability Company (SCRL) offers full ownership to foreigners with limited personal liability. Owners’ personal assets remain protected from company liabilities. Forming an SCRL comes with privacy advantages—shareholder names do not appear in public records. There is no required share capital for SCRL establishment, helping small businesses incorporate while maintaining limited liability. Foreign investors prefer SCRLs for self-management due to greater control without additional governing formalities.
Greater Access to Capital
Incorporating a corporation in Nicaragua improves access to capital. It enhances credibility, attracting investors more easily. The corporate structure supports good governance practices. This can boost investor confidence. Corporations have limited liability protection. Shareholders can invest without fearing losses beyond their investments. For the Sociedad de Responsabilidad Limitada (SCRL), there is no minimum authorized share capital needed. This simplifies capital formation for new businesses. Shares can be issued for cash or in-kind compensation, providing flexible options for raising capital.
Perpetual Existence
A common legal entity type in Nicaragua is the Sociedad Anónima (S.A.). This entity allows for perpetual existence, separate from its owners. Incorporating a Sociedad Anónima (S.A.) takes approximately 30 days, ensuring a streamlined process. Limited liability companies in Nicaragua, like the S.A., support ongoing operations beyond individual member lifespans. Electronic signatures are allowed in Nicaragua. They make transactions and agreements smoother, contributing to corporate stability. Nicaragua’s civil law-based framework supports perpetual existence for incorporated entities.
Disadvantages of Corporations
Branches of foreign companies in Nicaragua face operational hurdles. The lack of adequate regulation hampers business efficiency. These branches are often treated as anonymous societies. This treatment contradicts their true legal nature. Such misalignment causes significant inconveniences for businesses. Specific regulations for branches are absent. This leads to a forced adoption of inappropriate corporate structures. Without a proper legal framework, companies struggle to comply with local laws. Limited oversight from public institutions adds uncertainty. This results in potential legal risks for companies. Overall, these issues impact business operations in Nicaragua.
Formalities and Compliance Requirements
In Nicaragua, corporations must adhere to several formalities. The typical tax year runs from January 1 to December 31. However, businesses can request different fiscal year-end dates like March 31, June 30, or September 30. Corporations must appoint at least one director and two shareholders. The minimum paid-up share capital is as low as US$1. Share ownership transfers require a shareholder’s registration book endorsement. The Commercial Code mandates this process. The transfer must be inscribed in the Book of Registry of Shareholders, which remains private. Stamp duties apply, and sellers must declare income from sales in their annual tax return. Corporations must submit audited financial reports yearly. They also need to appoint an auditor to comply with requirements.
Double Taxation Issues
Nicaraguan tax laws impose double taxation challenges. The dividends withholding tax rate is generally 15%. This rate applies to dividends sent abroad by legal entities. Royalties paid to non-residents also face a 15% withholding tax. Payments to entities in tax havens incur a higher rate of 17%. Nicaragua does not levy a wealth tax. However, income from certain transactions may still be taxed. This depends on the recipient’s residency status. Profits repatriated to tax havens receive distinct tax treatment compared to non-tax haven countries. These taxation differences affect international business strategies.
Advantages of Limited Liability Companies (LLCs)
A Limited Liability Company (LLC) in Nicaragua offers many benefits. One major advantage is complete ownership for foreign investors, allowing full control of the business. This is appealing to those wanting a say in all operations. Additionally, LLCs do not require a minimum share capital. This means entrepreneurs with limited funds can start a business more easily. Privacy is another strong point. Shareholders’ names remain off public records, ensuring confidentiality. Furthermore, LLCs protect personal assets from business debts. This limited liability is crucial for managing risks effectively. The registration process for an LLC is also swift, typically taking up to one month.
Flexible Management Structure
In Nicaragua, business entities offer varied management structures. LLCs, in particular, have partners contributing capital through participation rather than traditional shares. This allows for flexibility in ownership. The Code of Commerce regulates business vehicles, ensuring they can adapt to diverse setups. Corporations in Nicaragua also provide a flexible structure, thanks to their share and governance setup. This adaptability makes them popular among businesses. For example, forming a Sociedad Anónima (S.A.) takes about 30 days, which is relatively quick. Foreign investors often maintain their existing corporate structures for continuity.
Pass-Through Taxation
Nicaragua uses a territorial basis for corporate income tax. This means only income earned within the country is taxed. The current corporate tax rate is 30%. However, income from abroad is not subject to this tax, which can be an advantage. Setting up a corporation in Nicaragua offers opportunities to engage in contracts that often need corporate structures. The tax system, overall, is medium in complexity. Compliance takes around 76 hours for labor tax obligations. Investment protection agreements provide tax exemptions and reductions, enhancing business advantages.
Easier Compliance Requirements
Starting a business in Nicaragua involves straightforward processes. The Code of Commerce clearly outlines shareholders’ rights, easing governance and compliance. A Sociedad Anónima (S.A.) can be incorporated in about 30 days. The civil law system facilitates digital transactions, allowing electronic signatures for documentation. This supports easy compliance. To ensure sustainable practices, Decree 20-2017 guides environmental evaluations. This helps businesses efficiently handle environmental regulations. The supportive legal framework encourages ventures in various sectors, making the system accessible for entrepreneurs.
Disadvantages of LLCs
In Nicaragua, establishing and managing a Limited Liability Company (LLC) brings challenges. One primary challenge is naming restrictions. The LLC must include at least one partner’s name in its legal name. This requirement limits business name flexibility.
The formation and registration of an LLC can be complex. It involves multiple steps, such as incorporation by a public notary. Registration with different authorities also adds complexity. While LLCs protect personal assets, they must have a local legal representative. This requirement increases operational duties and potential liabilities.
A lack of specific guidelines for foreign companies may complicate matters further. Foreign LLC branches may operate inconsistently with their true legal structure. This situation can create confusion and operational issues. Rigorous accounting requirements add another layer of challenge. They impose compliance burdens on the business.
Limited Life Span
Business entities in Nicaragua have different life spans. Corporations, known as sociedades anónimas, often have a perpetual lifespan. However, this is unless otherwise stated in their documents.
Limited Liability Companies, or sociedades colectivas de responsabilidad limitada, have a lifespan set by their partners. Branches of foreign companies, called sucursales de entidades extranjeras, tie their lifespan to their parent companies. If the parent company dissolves, the branch ceases to operate.
Foreign investors choose business entities based on liability and lifespan. The terms of these lifespans are in founding documents. They follow the Nicaraguan Code of Commerce.
Transferability Restrictions
Ownership transfer in a corporation in Nicaragua requires certain steps. Share transfers need endorsement in the shareholders’ registration book. This process can also include a sales and transfer contract between parties.
The corporation’s bylaws govern share transfer procedures. These rules might limit how transfers happen. All ownership changes must be recorded in the Book of Registry of Shareholders. This book serves as an internal transaction record.
The seller must report income from the sale on their tax returns. This requirement adds a financial aspect to the transfer process. Buyers must keep 10% of the transaction value for tax reporting. This step is a regulatory control on the transfer process.
To sum up, LLCs, while offering asset protection, face operational challenges in Nicaragua. The legal structure and lifespan considerations play a crucial role in their management and transfer processes.
Key Incorporation Aspects
Nicaragua’s main business laws date back to 1916 and were updated in 2022. However, they still provide limited rules for foreign company branches. These branches let companies work in Nicaragua without starting new structures, keeping control with the parent company. Foreign branches must register in the Commercial Registry and appoint a representative with full power of attorney. It takes about 30 days to set up a Sociedad Anónima (S.A.) and no minimum share capital is needed. Legal entities are under civil law, and electronic signatures are allowed during incorporation.
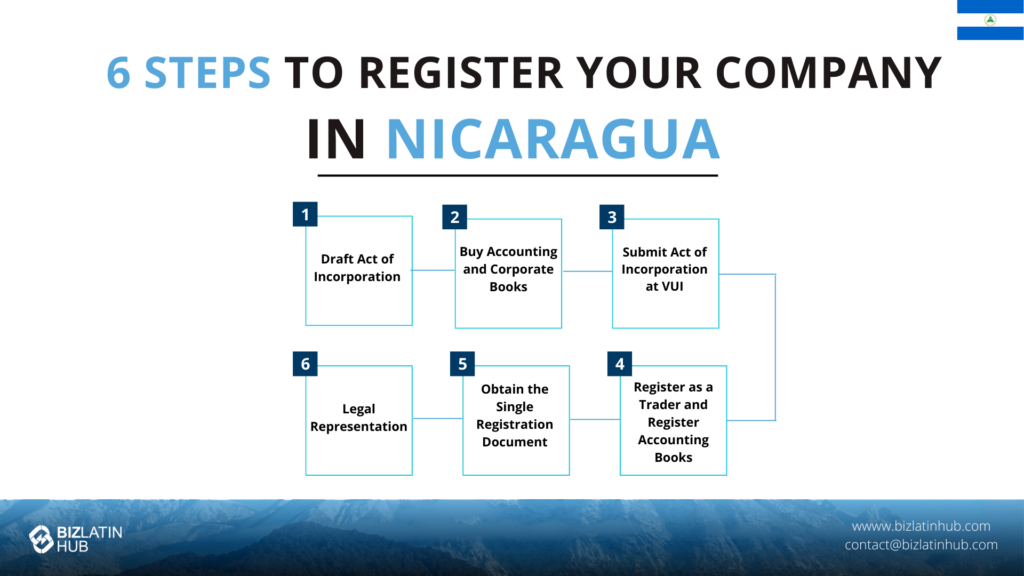
Shareholder and Director Requirements
In Nicaragua, a company needs at least two shareholders and one director. Directors’ names are not shown in the public registry. Corporate shareholders can own shares, and up to 100% foreign ownership is allowed. Directors must be shareholders. A corporate shareholder can appoint someone to represent it on the board. Annual meetings of shareholders are required to ensure good governance.
Incorporation Process Steps
The incorporation process starts with creating the company by Public Deed. Then, the company registers in the Public Mercantile Registry of the operating department. Once registered, the company is a recognized merchant. The company must also register essential books, like Minutes, the Share Registration Book, and accounting books. Appointing a Legal Representative is required. This person can be Nicaraguan or a foreigner with legal residency. All foreign documents must be apostilled and translated into Spanish. It takes about 30 days to set up a Sociedad Anónima (S.A.) with no minimum share capital.
Essential Records and Permits
To operate in Nicaragua, companies must obtain common records and permits as required by law. Additional records, registrations, and licenses are needed for regulated activities. The Commercial Code provides guidelines for company incorporation and necessary documentation. Owners should maintain essential legal documents as per Nicaragua’s civil law. Foreign companies often set up branches in Nicaragua, which also need specific records and permits.
Regulatory Landscape for International Transactions
The Nicaraguan legal system supports Corporations (SA) in engaging in international deals. These deals include mergers and asset purchases with Foreign companies. Corporations receive various tax benefits, making them favorable for international business activities. The Antitrust Law in Nicaragua protects local firms by monitoring international mergers to prevent market share issues. Corporations must structure public and private contracts to qualify for major projects and tenders. This not only broadens their operations but also builds trust among international partners.
Corporations must meet regulatory duties that ensure transparency and compliance with fiscal standards. These obligations foster reliable relationships with international suppliers and stakeholders. This trust is essential for smooth international transactions.
Role of Notaries in Business Formation
Notaries are vital in forming a business in Nicaragua. A Public Notary must notarize the social pact in a public deed. This step makes the corporation legally valid. The notarized pact, along with bylaws, must go to the National Registry. This submission is key to registering the business.
A Notary also authenticates the Articles of Incorporation. These documents define the company operations and the relationships among shareholders. Without a Notary, the business formation ignores Nicaraguan legal mandates, thus risking the business’s legitimate existence.
For the Legal Representative’s role, the Notary plays a crucial part. They register the appointment with the Mercantile Registry. This step involves granting a general power of administration immediately post-registration. The involvement of the Public Notary is essential for ensuring compliance with legal standards.
Compliance Requirements for Businesses
Compliance Requirements for Businesses in Nicaragua
Businesses in Nicaragua must adhere to several compliance requirements. The corporate tax rate is 30%, while the value-added tax (VAT) is 15%. Both local companies and branches of foreign companies, known as permanent establishments, face the same tax obligations.
Incorporating a Sociedad Anónima (S.A.) typically takes 30 days. There is no minimum share capital needed for this process. According to the Nicaraguan Code of Commerce, shares in corporations grant equal rights to shareholders, unless specified otherwise in the articles of incorporation.
Key Compliance Points:
- Corporate Tax Rate: 30%
- Value-Added Tax (VAT): 15%
- Incorporation Time for S.A.: 30 days
- Share Capital Requirement: None for S.A.
- Shareholder Rights: Equal unless stated
These requirements ensure businesses operate within the legal framework. Companies must maintain accounting books and submit tax returns to comply with Corporate Law.
How Biz Latin Hub Can Help
Understanding and navigating Nicaragua’s business structures can be complex, but Biz Latin Hub specializes in providing comprehensive market entry and back-office solutions to simplify the process. From incorporating your business and ensuring legal compliance to managing taxation and accounting, their team of local and international experts ensures you establish a strong foundation for success. If you’re ready to start or expand your business in Nicaragua, click here to reach out to Biz Latin Hub.